Chemiluminescence Applications
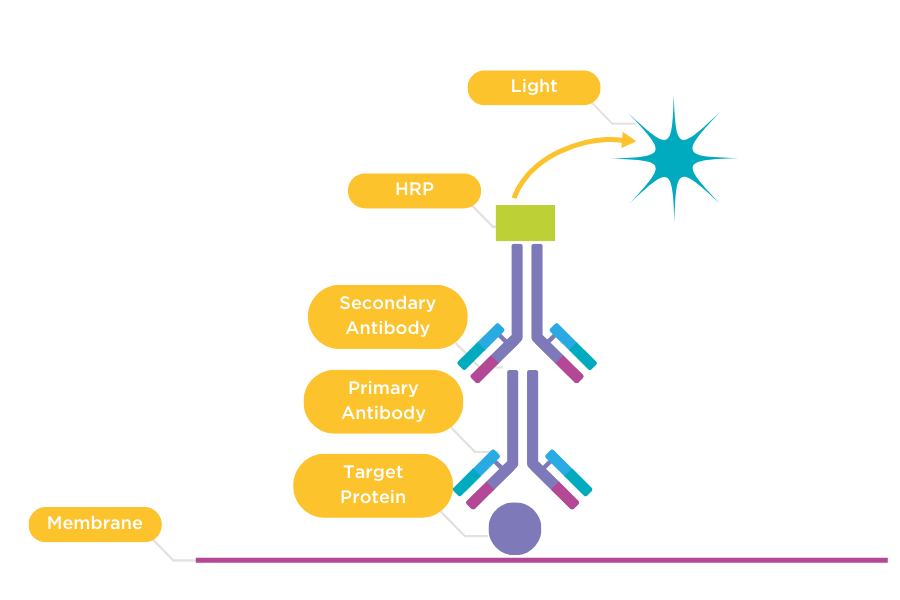
Chemiluminescence is a non-radioactive detection method based on a chemical reaction that produces visible light. In chemiluminescent western blotting, this occurs when a chemiluminescent substrate attached to an antibody bound to your target protein undergoes an enzyme-mediated reaction. This approach offers greater sensitivity than colorimetric detection, as the antibody provides target specificity and the enzyme amplifies the light signal.
Common chemiluminescent methods include ECL, where horseradish peroxidase (HRP) oxidises luminol, and CDP-Star®, where a 1,2-dioxetane compound is dephosphorylated by alkaline phosphatase. Bands can be visualised using traditional X-ray film or modern cooled CCD-based imaging systems, with digital capture providing faster, more convenient results. The high photon output of chemiluminescent reactions allows detection of proteins expressed at very low levels when combined with appropriate imaging technology.
Chemiluminescent Western Blotting
Chemiluminescent western blotting is the best technique if you need highly sensitivity detection of a single protein. Using a dedicated chemiluminescence CCD-based system, like the GeneGnome XRQ for imaging your chemiluminescent Western blots, gives you wider dynamic range than film, allowing you to safely and accurately detect and analyse picogram and even femtogram levels of protein.
With the GeneGnome XRQ system’s powerful GeneSys software you simply select the chemiluminescent substrate you are using, the system then automatically captures your choice of one or a series of images, ensuring you’ll effortless produce a perfectly exposed image, without using any film.
If you’re looking for a system, which can image chemiluminescent and fluorescent western blots, the G:BOX Chemi or G:BOX mini systems are a perfect choice.