Syngene has partnered with AirClean systems to offer a safe and reliable range of enclosures, hoods and cabinets. These systems work to create a safe and clean environment that protects both the operator and the process. With a wide variety of PCR cabinets available, knowing which one you need can take time and effort.
The most popular PCR cabinet versions are PCR and Dead Air workstations. It is essential to understand the differences between the two workstations and know which one suits the work procedures you carry out. Selecting the right workstation ensures reliable lab results and increases efficiency.
What is a PCR workstation?
PCR workstations are used in life sciences and molecular biology labs to prevent cross-contamination between samples. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) involves amplifying and replicating millions and billions of copies of a specific segment of DNA. It is, therefore, essential to prevent cross-contamination from the air and equipment contaminants such as pipettes, pipette tips, tube racks and PCR tubes.
The primary purpose of a PCR workstation is to provide an enclosed space that prevents cross-contamination. The environment must remain sterile throughout the duration of the PCR procedure. The workstation is enclosed on three sides with a sash on the front that allows the operator’s arms to access the workspace.
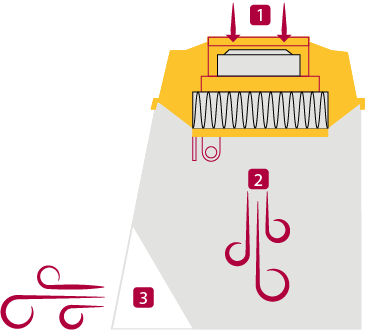
High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are used to eliminate airborne contaminants. HEPA filters have a 99.997% efficiency at 0.3 microns. The UVTech controller ensures the filter is always working at peak performance and alerts the operators once it needs to be replaced.
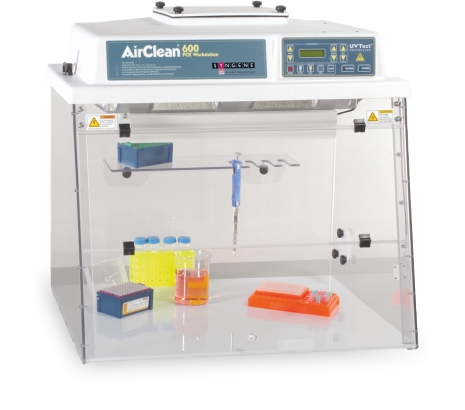

The system is also fitted with a UV-light timer. This shelf is for the sterilisation and irradiation of equipment for aseptic techniques. With the sash safety switch, the UV light is automatically turned off to protect the technician if the station is in use.
- Most PCR workstations use a laminar flow arrangement where room air enters and is cleaned by a pre-filter.
- The air then moves down through the HEPA filter.
- Clean vertical laminar flow air enters the chamber and then recirculates clean air into the room.
Dead air boxes are similar to PCR workstations which is why customers often need clarification on which system fits their needs. Both systems look similar as they are enclosed on three sides and have a sash at the front for operator access. They also have UV sterilisation for UV decontamination of the workspace and equipment.
The main difference between a dead air box and a PCR workstation is that in a dead air box, the air is ‘dead’, meaning no airflow is created. This circulation-free environment still reduces the chance of air particulates coming into contact with your sample. This ‘dead air’ is perfect for the amplification and manipulation of DNA/RNA.
Both workstations are used for preventing cross-contamination between samples and offer a way of quickly sterilising the work area and equipment with UV light. Still, the dead air box does not protect against environmental contamination during the experiment. Therefore, you will only require a dead air box if you do not require the most sensitive detection of DNA/RNA segments and a contamination-free environment.
If you want to know which system suits your unique needs, please contact sales@syngene.com for more support. Want to see the full AirClean range? Click here and head over to the Syngene website.
